General Notes for Standard Studding Outlet Manufacturing
GENERAL NOTES FOR FCI STANDARD STUDDING OUTLETS
CODES: FCI Studding Outlets are manufactured in compliance with ASME Section II, Section VIII, Div. 1, and ASME B16.5. Products may be ordered to special requirements or other standard codes such as ASME Section I, III and Section VIII, Div. 2,ASME B31.1 or B31.7.
MATERIALS: All materials comply with the applicable ASME and ASTM specifications. Full traceability is mandated by our quality system. Standard forged material is carbon steel SA105. Connections can also be furnished in other carbon steels, alloy steels, stainless, high nickel and non-ferrous alloys upon request.
BORES: Standard studding outlet bores are equal to their nominal flange/pipe size. Special bores are available upon request.
FACING: Standard facing is raised face to ASME B16.5. The 0.06″ raised face is included in thickness “T” for Class 150 and 300 studding outlet connections. The 0.25″ raised face is included in thickness “T” for Class 600, 900, 1500 and Class 2500 studding outlet connections. Other standard and special facings are available.
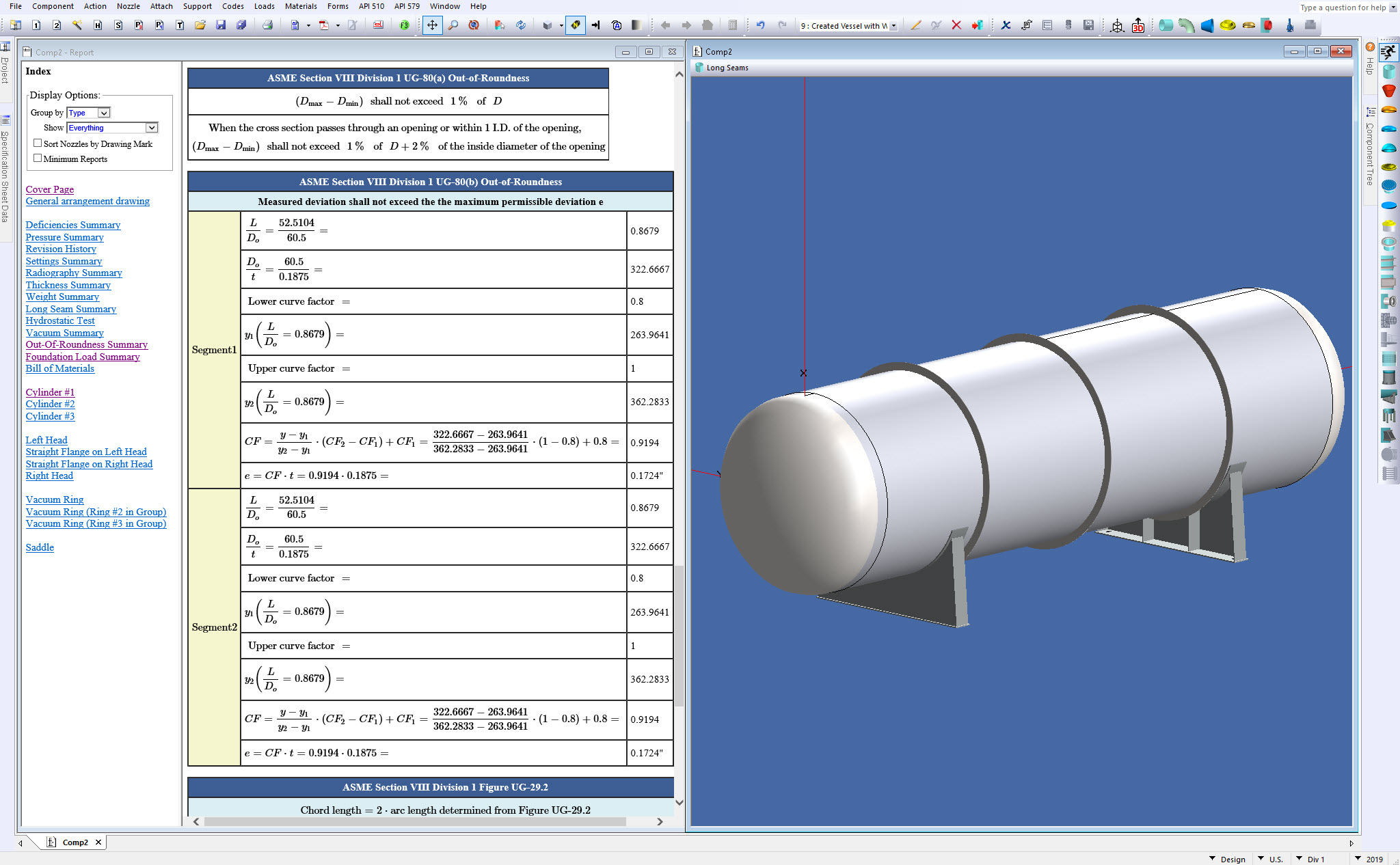
The 80-10 is typically only 66% the thickness of the ASME Torispherical. The Ellipsoidal head is slightly thinner, but cost savings will be offset by added labor cost and a larger blank size. The 80-10 head, developed by Brighton Corporation, meets all the requirements of the ASME Unfired Pressure Vessel Code. UG-80 (a) 2.6: out-of-roundness for external pressure: UG-80 (b) 2.7: head skirt length. UG-44, Table U-3: 3.10: flanges: ASME B16.5: PT Rating @ design temp. UG-80 and UG-81 Permissible out-of-roundness of cylinders, conical sections, spheres, and formed heads Out-Of-Roundness calculations are now available for cylinders, conical sections, spheres, and formed heads. The calculations can be disabled by the option switch Include Out-Of-Roundness Calculations (UG-80) in the ASME Codes dialog. UG-80 and UG-81 COMPRESS automatically provides out-of-roundness tolerances that must be maintained during pressure vessel fabriaction. Pressure Relieving Devices. The Introduction to ASME B31.3 states 'It is the owner's Design Authority responsibility to determine which Code Section is most applicable to the piping installation.” The other ASME B31 Code Sections and other common National Consensus Codes are listed in Table 1.
THICKNESS: Listed thickness “T” dimensions in FCI charts are the minimums required per ASME Section VIII Div. 1 for thread engagement and thickness required for installing studding outlets to the inside diameter of vessel shells, heads, cones, pipes, etc. as shown in Figures A, B, C, and D of typical attachment styles for studding outlet connections.
For “through—type” installations as per Fig. B and per Fig. C, thickness “T” must generally be increased in accordance with the requirements of the ASME Code, Section VIII, Div. 1, paragraph UG-43(d), to provide additional material under the drilled and tapped holes of the studding outlet.
Surface mounted “set-on” studding outlets, as shown in Figures E, F and G, generally require a thickness less than that listed in accordance with ASME Code design.
Studding outlets will be priced and produced to other than the FCI listed thickness “T” at Purchaser’s request. See following page of other studding outlet mounting configurations to determine thickness “T”.
In all cases, Purchaser shall design and advise FCI of the required thickness “T” dimension.
BODY: Studding outlet body outside diameters are equal to the outside diameters of flanges, as specified in ASME B16.5 for the size and class of connection ordered. Upon request, studding outlet outside diameters may be increased to satisfy reinforcing requirements. Standard FCI studding outlet mating connection ends will be manufactured in accordance with ASME B16.5 flange and drilling dimensions, Drilled holes will be tapped in accordance with ASME Section VIII, Div. 1, paragraph UG-43(g). Bolt holes will straddle natural centerlines, unless specified otherwise.
Studs, bolts, nuts, and gaskets are not furnished.
CONTOURED BOTTOMS: Studding outlet connections will be furnished with flat bottoms unless specified otherwise. All connections are available with optional “contoured” bottoms for installation in shells, heads and cones. In these cases, the minimum thickness “T” will be measured from the studding outlet face to the bottom contour of the connection. See preceding thickness note and typical attachment style as shown on following page.
Tolerance for bottom contouring will be in accordance with ASME Section VIII, Div. 1, and paragraph UG-80 out— of-roundness tolerance. Purchaser to specify when connections are to be surface mounted for special contouring requirements, such as Fig. F and Fig. G.
Wrap around” connections exceeding the outside diameter of the shell to which they are mounted will have the transverse pendant points square cut.
Tangential/hillside, inclined, and other special contoured bottoms are available upon request.
INSERT LIPS: All studding outlet connections can be ordered with insert lips- “Q” type attachment.
TEST HOLES: Studding outlets may be ordered with test holes. Unless specified otherwise, test holes will be provided in accordance with Fig. E, ¼” diameter drilling and tapped with a 1/8″ N.P.T.
HEAT TREATMENT: All standard connections over Class 300 rating are supplied in the normalized condition in accordance with the requirements of ASME Section II. Other heat treatment requirements can be provided upon request.
TOLERANCE: Manufacturing tolerances, as a minimum, will meet the requirements of ASME B16.5 where applicable.
REINFORCEMENT: Reinforcement must be provided to satisfy area requirements for all planes through the center of the opening normal to the vessel surface especially the voids created by the drilled and tapped holes of studding outlets. The area requirements, planes of reinforcement and the “F” factor are to be addressed by Purchaser’s designer in accordance with the ASME Code, Section VIII, Div. 1, paragraph UG-37. Increasing the thickness “T” and/or the outside diameter of the studding outlet connection may replace the area lost from the drilled and tapped holes. See following table for
area loss of FCI standard studding outlet drilled and tapped holes:
TAP SIZE (inches) | DEPTH OF HOLE (inches) | AREA (sq. inches) |
1/2 | 0.88 | 0.81 |
5/8 | 1.12 | 1.28 |
3/4 | 1.31 | 1.80 |
7/8 | 1.44 | 2.29 |
1 | 1.56 | 2.82 |
1 1/8 | 1.81 | 3.69 |
1 1/4 | 2.12 | 4.83 |
1 3/8 | 2.25 | 5.62 |
1 1/2 | 2.38 | 6.47 |
1 5/8 | 2.56 | 7.53 |
1 3/4 | 2.81 | 8.92 |
1 7/8 | 3.00 | 10.19 |
2 | 3.31 | 12.04 |
2 1/4 | 3.56 | 14.50 |
2 1/2 | 4.00 | 16.13 |
2 3/4 | 4.38 | 21.82 |
3 | 4.62 | 25.02 |
3 1/2 | 5.38 | 33.99 |
Contact Us for Studding Outlet Manufacturing
Forged Components is globally recognized for studding outlet manufacturing. As one of the leading pressure vessel connection companies, we provide expert assistance to begin your project. Contact us at (281) 441-4088 or email us at sales@forgedcomponents.com.
CalQlata's pressure vessel calculator determines the minimum permissible wall thickness(es) or maximum permissible pressure(s) for spherical or cylindrical pressure vessels and their heads (Fig 1) that ...
... are subject to internal pressure, or
... subject to external pressure, and
... conforms to ASME VIII, Division 1 design code
CalQlata's pressure vessel calculator does not include non-circular pressure vessels
The minimum required wall thickness of pressurised spheres and cylinders could be determined using classical theory but this is not normally considered appropriate for the safety of pressure vessels, which usually contain considerable levels of stored energy⁽¹⁾ and are frequently in close proximity to operating personnel. Moreover, physical collapse due to external pressure is always as a result of elastic instability and far too difficult to predict using general mathematical principles. ASME's considerable long-term experience provides far greater confidence in minimising the likelihood of unexpected collapse, given certain design criteria and limitations.
Shape
The cross-section of any internally or externally pressurised vessel (container) should be circular for maximum pressure-carrying capacity and/or stability. Moreover, it should have no irregularities, corners or flat surfaces.
A pressure vessel is a container of any size and shape that will maintain its integrity (but not necessarily its size and shape) against an internally or externally pressurised fluid. A properly designed pressure vessel is one that will do so with no risk of damage, and the ASME VIII design code is generally considered to be the most appropriate means of achieving this.
Cylinder
Any longitudinal container will naturally try to form a cylinder under sufficient internal pressure. Its length will have no effect on stresses induced in an internally pressurised vessel other than those induced by its support.
Pressure Vessels calculates the wall thickness of plain cylinders of same material and equal wall thickness throughout. If you wish to evaluate cylindrical pressure vessels of different diameter and material the wall thickness of each section should be calculated separately. Conical Head calculations may be used to evaluate conical transitions between each diameter variation, along with any necessary reinforcement.
ASME VIII only considers membrane stresses (longitudinal and circumferential) in a cylindrical vessel, i.e. radial stresses are ignored, which is considered reasonable given that the maximum radial stress (equal to the internal pressure) is insignificant compared to membrane stresses in a thin-walled cylinder.
Cylindrical vessels will always need a thicker wall than a sphere for any given diameter and design pressure.
Sphere
Fig 2. Typical Heads
Any bulk container will naturally try to form a spherical shape under sufficient internal pressure.
Pressure Vessels calculates the wall thickness of plain spheres of same material and equal wall thickness throughout.
ASME VIII only considers membrane stresses (circumferential) in a spherical vessel, i.e. radial stresses are ignored, which is considered reasonable given that the maximum radial stress (equal to the internal pressure) is insignificant compared to membrane stresses in a thin-walled cylinder.
Spherical vessels will always need a thinner wall than a cylinder for any given diameter and design pressure, which is why very large pressure vessels tend to be spherical.
Heads
A cylindrical vessel head is a closure, lid or cap (Fig 2) of consistent material and wall thickness throughout except as described in Skirt and Knuckle below
Skirt is a cylindrical section that forms the interface to the cylinder or connection flange, the wall thickness of which should be at least the same as the vessel to which it is attached. All head volumetric calculations include a skirt length equal to the minimum value recommended by ASME of;
3 x wall thickness + half an inch.
Knuckle is a radiused transition between the head and the skirt of diameter at least 6% of the skirt diameter. Whilst the minimum calculated material thickness for transition knuckles according to the ASME VIII design code is generally less than the calculated minimum wall thickness for the head and cylindrical vessel, Pressure Vessels assumes this wall thickness to be the same as its head for volumetric calculations.
Hemispherical is a hemisphere with the same diameter as its skirt. No knuckle is required for these heads.
Ellipsoidal is half an ellipse where the head depth (minor axis) is equal to one quarter of the skirt diameter (major axis). No knuckle is required for these heads.
Torispherical has a crown (segment of a sphere) radius equal to the skirt diameter and a transition knuckle.
Toriconical is a simple cone with a knuckle transition at its skirt. ASME VIII does not limit the included angle of internally pressurised toriconical heads⁽²⁾
Conical is a simple cone that finishes at the vessel with a sharp transition. No knuckle is required for these heads but reinforcement may be required inside the interface. ASME VIII recommends that the included angle of internally pressurised conical heads does not exceed 60°⁽²⁾
Pressure
The design pressure of any pressurised container is the difference between the internal and external pressure. For example; if a pressure vessel is exposed to an internal pressure of 100psi and an external pressure of 35psi, the design pressure for the vessel will be an internal pressure of 65psi (65 = 100 - 35)
Internal and external pressures should include the effects of head-pressure (pressure due to fluid depth), especially if the pressurising fluid is a liquid, and as head-pressure varies with depth the design pressure at the top of a liquid container need not be as great as that at its base.
For example; if a 500 inch diameter vessel is 90% filled with a fluid of density 0.0362lb/in³ and an over-pressure of 30psi is applied at the surface of the liquid, the maximum pressure at the top of the vessel will be 30psi whilst the maximum pressure at its base will be 46.29psi
(46.29 = 90% x 500 x 0.0362 + 30)
Internal (pressure)
A shell or cylinder of constant material quality and wall thickness exposed to internal pressure will always equalise hoop, radial and longitudinal stresses throughout⁽³⁾, and failure will occur due to the combined effect of these stresses exceeding UTS.
Maximum possible pressure without inducing permanent deformation will occur immediately prior to the combined stress reaching yield.
Maximum allowable pressure is that which induces an allowable stress (σₐ), which is a specified fraction (< 1.0) of yield stress and generally referred to as material utilisation.
External (pressure)
A shell or cylinder of constant material quality and wall thickness exposed to external pressure will always deform as a result of elastic instability⁽⁴⁾. Failure will occur when a change in shape is sufficient to concentrate stresses such that yield stress is exceeded locally prior to expectations.
In all vessel shapes, the level of instability is entirely due to the ovality of the manufactured section. The greater the out-of-roundness, the quicker⁽⁵⁾ the shell will collapse.
Ring Stiffeners (cylinders & external pressure only)
Internal and/or external stiffening rings (Fig 3) increase elastic stability and are often installed at regular intervals in externally pressurised vessels to minimise wall thickness. You can minimise total vessel weight by optimising stiffener; material, section and longitudinal spacing. However, to eliminate galvanic corrosion and improve weldability the pressure vessel calculator assumes stiffener material to be the same as that of the vessel wall.
Stiffeners are added to internally pressurised vessels only to accommodate localised loading due to supports, closures, openings, etc., they will not affect wall thickness.
Reinforcement stiffeners are not included in vessel volume calculations.
Welding
As all pressure vessels must to be welded using certified materials and coded welders, weld joint factors (WJF) between 0.9 and 1.0 are the norm in their design.
Variable Plate Thickness
Whilst there is little to be gained from varying the wall thickness of small pressure vessels and those that contain gas, the weight and cost of large vessels and those that contain liquids can be lessened significantly by reducing the wall thickness with head-pressure (see Pressure above). Moreover, the lower centre of gravity of large pressure vessels with a wall thickness that reduces with height will improve stability during an earthquake. This technique may be applied to both cylindrical and spherical vessels.
ASME VIII
The world's most recognised design code for pressure vessels comprises two Divisions;
Division 1 (mandatory rules): For all pressure vessels including those covered by Division 2, and;
Division 2 (alternative rules): For fixed pressure vessels
The ASME VIII code provides design, manufacture and inspection rules for all pressure vessels and their head(s) along with the requirements for shape variations, nozzles, closures, openings and reinforcement.
CalQlata's pressure vessel calculator includes cylindrical and spherical shells and heads according to Division 1, Part UG and Appendices 1 & 5.

Included in the code is a single 3D plot (Dₒ/t vs L/Dₒ vs A for externally pressurised vessels) used to identify ASME's Factor A, along with about 60 material charts (Appendix 5, Fig 5-UCS-28.1 to UCD-28) that identify ASME's Factor B (and elastic moduli) for various materials at specific temperatures.
For maximum accuracy, CalQlata has mathematically modelled each plot on every chart, all of which have been included in the pressure vessel calculator along with interpolation.
Fig 5 (Appendix 5)
This sub-section (Fig 5) applies only to pressure vessels exposed to external pressure.
Refer to Mandatory Appendix 5, Fig 5 (material charts) below for material chart titles
Fig 4. ASME VIII Fig 5 UCS-28.6 @ 300°F
Fig 5 titles refer to the following materials:
UCD: Sub-section C, Ductile Cast Iron
UCI: Sub-section C, Cast Iron
UCS: Sub-section C, Carbon Steel
UHA: Sub-section C, Austenitic Stainless Steel
UHT: Sub-section C, Heat-Treated Carbon Steel
UNF: Sub-section C, Non-Ferrous Metal
The plots included in this group of ASME figures are logarithmic interpretations of a modified version of the stress-strain curve for each metal concerned. The horizontal axis (A) is base 10 and the vertical axis is a natural base
Logarithmic and non-logarithmic versions of the plot for UCS-28.6 @ 300°F are provided in Fig 4 for comparison purposes, where it can be seen that above a relatively low stress (B) a minor increase is expected to induce a significantly greater strain (A) than would otherwise be expected for the same material in tension or linear compression. ASME expects the maximum permissible stress in an externally pressurised vessel manufactured from this metal to be approximately a ¼ of that for an internally pressurised vessel.
I.e. 'A' is nominally defined by ASME as; 0.125÷(Dₒ/t)⁽⁶⁾. The relationship 'Dₒ/t' is the reciprocal of strain in a curved vessel wall (e = y/R), where 'Dₒ' is the outside diameter of the vessel, 'R' is its radius, 't' is its wall thickness and 'y' represents half the wall thickness or the distance from the neutral axis to the outer fibre of the vessel wall. Therefore, 'A' represents ⅛ᵗʰ the expected strain.
Twice the value of Factor 'B' is used in the allowable stress calculations⁽⁶⁾. Therefore applying one eighth of the strain with twice the stress means that ASME expect elastic instability to occur at one quarter of the material's tensile yield stress.
You are permitted to use any portion of each plot. The maximum value indicated for 'B' on any plot is regarded by ASME as the yield stress associated with elastic instability. Any further increase in 'B' and you can expect elastic instability to increase the risk of localised plastic strain with little increase in stress (see Fig 4)
The maximum allowable stresses are similarly reduced for all ASME VIII-Fig 5 metals used in the manufacture of externally pressurised vessels.
Verification
You can verify CalQlata's mathematical modelling of ASME's plots for factor 'B' (Division 1, Appendix 5, Figs UCS-28.1 to UCD-28) using the co-ordinates provided below the 'Output Data' in the Data Listing window (Fig 5). One plot is provided where interpolation has been unnecessary, otherwise two plots are provided; one at the temperature above that entered and one below.
Verification using your preferred spreadsheet (e.g. Microsoft's Excel) can be performed as follows:
1) Scan-Copy the appropriate Fig-5 chart from ASME VIII and Insert into a worksheet
2) Copy one set of co-ordinates from the pressure vessel calculator
3) Paste the co-ordinates into the same worksheet as the copied chart image (1 above)
4) Select the co-ordinates
5) Select menu item 'Insert' > 'Chart' > 'Scatter' > 'with straight lines' (generate the chart)
6) Set the horizontal axis to logarithm base 10
7) Set the vertical axis to logarithm base 2.7
8) Drag the plot over the copied chart image (1 above)
9) Resize the generated chart (5 above) to fit the axes of the copied chart image (1 above)
You may repeat the above procedure for the second set of co-ordinates when provided.
An example verification plot is provided in Fig 5 where the verification plot (pale-blue dotted line) is overlaid ASME's plot (pink line).
Example Calculation 1
What wall thickness(es) would be acceptable for an 800 inch diameter spherical vessel manufactured from SA-283-D (Table UCS-23) that contains water (ρ = 0.03613lb/in³) up to a maximum depth of 750 inches with an over-pressure of 2bar (29.4psi, 0.2N/mm²)?
Head pressure = 750 x 0.03612729 = 27.1psi)
Total pressure: at the bottom of the vessel = 27.1 + 29.4 = 46.5psi
Total pressure: at the top of the vessel = 29.4psi
Fig 6. Large Sphere

If manufactured from 160in (high) steel plate, weld seams will occur at the heights indicated in Fig 6 and the following Table:
The depth of liquid at the bottom of each plate is calculated thus:
d = D - R.{1 - Cos(L/R)}
and the total pressure at each depth 'd' is calculated thus: p = ρ.d₃ + pₒ
where:
D = total liquid depth (750ins)
R = vessel radius (400ins)
L = arc length of plate(s) from base (160ins)
ρ = fluid density (0.03613lb/in³)
d = liquid head (depth at bottom plate)
pₒ = over-pressure (29.4psi)
p = total pressure (46.5psi)
Fig 6 shows the calculation dimensions for the 3rd plate-level
You will need to calculate the plate thickness for each pressure level assuming the entire vessel is exposed to the pressure concerned. The following calculations (per level) are based upon an allowable stress of 12,700psi:
| Plate | Arc length | Liquid depth | Total pressure | Plate thickness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| level | (L) ins | (d) ins | (p) psi | (t) ins | |
| top | 8 | 1256.64 | -50# | 29.4 | 0.087 |
| 7 | 1120 | -26.89# | 29.4 | 0.087 | |
| 6 | 960 | 55.04 | 31.389 | 0.093 | |
| 5 | 800 | 183.54 | 36.031 | 0.107 | |
| 4 | 640 | 338.32 | 41.624 | 0.123 | |
| 3 | 480 | 494.94 | 47.282 | 0.140 | |
| 2 | 320 | 628.68 | 52.114 | 0.154 | |
| bottom | 1 | 160 | 718.42 | 55.357 | 0.164 |
# Overpressure (pₒ) only apply to these plates as the surface of the liquid falls below the bottom of the plates concerned.
You could alter the plate thickness for each stratum or multiples thereof. However, the thickness selected for each level must be suitable for the bottom of its lowest plate. The above table also shows that if the vessel were to be manufactured from a single plate thickness it must be no less than 0.164inches (4.2mm).
Whilst the above calculation procedure may also be applied to externally pressurised vessels, plate thickness variations may exacerbate elastic instability.
Example Calculation 2
A typical practical use for externally pressurised vessels is mid-water support buoys. These use their buoyancy to support a weight, e.g. risers, cables, measuring equipment, etc. above the seabed.
Ug-80 Asme Pdf
Question: A cylindrical buoy of minimal mass is required to lift 4000lbf (total capacity) and operate in seawater at a depth of 325ft. What would be the dimensions of a suitable steel buoy (ignore the effect of vessel heads for this example calculation)?
Assuming the buoy is manufactured from the same material as used in Example 1 (above), the maximum allowable stress will be 12,700psi.
The external pressure at this depth would be 144.4psi, which is also the differential pressure as it is assumed that atmospheric pressure (1 bar) is inside the vessel.
The buoy's lift force can be calculated thus:
Fᴸ = ρʷ x Vₒ - ρˢ x (Vₒ - Vᵢ)
Enter this formula into your preferred spreadsheet referencing the appropriate output data you copy and paste from Pressure Vessels.
A typical calculation procedure is listed below (Fig 7):
Step 1. Enter your preferred material thickness (t)
{e.g. 0.512 inches}
Step 2. Alter the internal diameter (Øᵢ) until you have exceeded the pressure (p) required for the depth
{e.g. 166.6 psi}
Step 3. Alter the length (L) and iterate until you have exceeded the required lift force (4000lbf)
{e.g. 74 ins} see Anomaly 1 below
Step 4. Iterate the number off and cross-sectional area of the ring stiffener until you achieve an acceptable alternative wall thickness
{e.g. 0.252 ins} see Anomaly 2 below
Step 5. If you prefer to use a cylinder with stiffening rings, then recalculate the mass of the buoy with your preferred stiffening rings and modify the lift force accordingly.
The lift force of the cylinder in Fig 7 is ≈4,218lbf (you may continue to iterate to optimise all properties if you wish)
You may notice some anomalies in your results when making small changes to the input data in Pressure vessels:
Anomaly 1: Small increases to the diameter (Øᵢ) without increasing thickness or length may result in an unexpected increase in design pressure.
This is due to the fact that whilst a minor increase in 'Dₒ/t' will reduce Factor 'A' in Fig UG-28-0, the coincident reduction in 'L/Dₒ' will increase it and you may find that 'L/Dₒ' has a greater effect on your results than 'Dₒ/t'. This is not an error in the code, it is simply due to the way in which the code works. According to the design code, the resultant higher design pressure is perfectly reasonable.
Anomaly 1: Adding stiffeners to a vessel increases the wall thickness.
This is due to the significant difference between '4 x B' and '2 x E x A' in UG-28 (c) Steps 6 & 7 either side of a temperature boundary in the Fig 5 plots. You will usually find that increasing the cross-sectional area and/or number of stiffening ring(s) will reduce the modified wall thickness (tᵣ) to an acceptable value.
It is usual to fill and pressurise buoys with an inert gas, such as N₂ so that the buoy operates at zero stress; i.e. differential pressure is zero and its external pressure carrying capacity is normally designed for transient conditions.
Pressure Vessel Calculator – Technical Help
A warning will be displayed if any wall thickness exceeds the maximum value (relative to shape radius) recommended by the design code or if the wall thickness falls below 0.0625 inches as ASME VIII does not cover pressure vessels with wall this thin.
Units
Input data are required in Imperial: inches (ins), pounds (lbf) and degrees Rankine (°R) in order to ensure no conflict with the design code. All input and output data are converted to metric units.
Conical Heads
A 'conical' head requires no knuckle so if a value is entered for the knuckle radius (i.e. rᵢᵏ > 0) the pressure vessel calculator will assume you are looking for a 'toriconical' head and calculate the wall thickness accordingly. If you are looking for the wall thickness of a plain 'conical' head, you must set the knuckle radius to zero (i.e. rᵢᵏ = 0).
Unless special analysis demonstrates to the contrary, ASME VIII does not recommend plain conical heads with an included angle greater than 60° (see Heads above), therefore if you enter a knuckle radius (rᵢᵏ) of 0 and half the included angle ('α') > 30, the pressure vessel calculator will display a warning message that only toriconical cone heads are valid for this angle. In such a case, you must either modify the angle to less than 30 or a enter a value for the knuckle radius in order to generate a valid 'tᶜ' value.
When a value of zero is entered for the knuckle radius (i.e. rᵢᵏ = 0) the pressure vessel calculator will always check to see if reinforcement is required for wall thickness 'tᶜ'. If it is required, the cross-sectional rea of the reinforcement is provided alongside the 'tᶜ' result {A=?}. The sectional shape and position of the reinforcement is up to you, however, ASME recommend a maximum permissible distance from the transition (between the cylinder and the cone) for the centroid of area of this reinforcement. The formula for calculating this distance is provided in the Technical Help page of the program.
Input Data
Vessels and heads are calculated slightly differently dependent upon the applied pressure whether it is internal or external.
Internal Pressure
You enter the desired pressure rating ('p') and Pressure Vessels calculates the minimum permissible wall thickness ('t') according to the ASME design code.
External Pressure
You enter the expected wall thickness ('t') and Pressure Vessels calculates the maximum permissible pressure ('p') according to the ASME design code. This method may require one or two iterations to achieve the desired pressure rating.
Ṯ (temperature): of the pressurising fluid
Aᵣ (cross-sectional area): of the ring stiffener in cylindrical vessel
№ (number): of stiffeners in cylindrical vessel, spacing will be based upon full pitches between all stiffeners. Pitch = L ÷ (№ + 1)
L (length): cylinder length, excluding heads
Common Data
Øᵢ (outside diameter of vessel): the maximum value including ovality
σₐ (maximum allowable stress): for the selected material according to ASME VIII, Division 1, Sub-section C, Tables UCS-23 to UHT-23

WJF (weld joint factor): between 0.9 and 1.0 should be used unless unknown or inferior welding procedures are used in the vessel's manufacture
α (half included angle ): of conical and toriconical heads
rᵢᵏ (knuckle radius-inside): for torispherical and toriconical heads
Output Data
Internal Pressure
t (wall thickness): minimum permissible value for a cylindrical or spherical vessel
tᵉ (wall thickness): minimum permissible value for an ellipsoidal head
tᵗ (wall thickness): minimum permissible value for a torispherical head
tʰ (wall thickness): minimum permissible value for a hemispherical head

tᶜ (wall thickness): minimum permissible value for a conical head
tᵏ (wall thickness): minimum permissible value for a transition knuckle
External Pressure
p (external pressure): maximum permissible value for the vessel
pᵉ (external pressure): maximum permissible value for an ellipsoidal head
pᵗ (external pressure): maximum permissible value for a torispherical head
pʰ (external pressure): maximum permissible value for a hemispherical head
pᶜ (external pressure): maximum permissible value for a conical head
A (ASME factor): equivalent strain interpolated
B (ASME factor): equivalent stress interpolated
σ₅ (yield stress): of the vessel, head and stiffener materials based upon ASME VIII, Division 1, Appendix 5, Figs UCS-28.1 to UCD-28 at the design temperature ('Ṯ')
Iᵣ (second moment of area): minimum value for the ring stiffener for the vessel dimensions and material (excluding vessel wall)
E₅ (Young's modulus): of the vessel, head and stiffener materials based upon ASME VIII, Division 1, Appendix 5, Figs UCS-28.1 to UCD-28 at the design temperature ('Ṯ')
Common Data
Vᵢ (internal volume): of a cylindrical or spherical vessel (excluding reinforcement stiffening rings)
Vₒ (external volume): of a cylindrical or spherical vessel (excluding reinforcement stiffening rings)
Vᵢᵉ (internal volume): of an ellipsoidal head including skirt
Vₒᵉ (external volume): of an ellipsoidal head including skirt
Vᵢᵗ (internal volume): of a torispherical head including knuckle and skirt
Vₒᵗ (external volume): of a torispherical head including knuckle and skirt
Vᵢʰ (internal volume): of an hemispherical head including skirt
Vₒʰ (external volume): of an hemispherical head including skirt
Vᵢᶜ (internal volume): of a conical or toriconical head including knuckle (toriconical only) and skirt
Vₒᶜ (external volume): of a conical or toriconical head including knuckle (toriconical only) and skirt
Verification Co-ordinates
Factor 'A' is calculated for ellipsoidal, torispherical and hemispherical heads so no verification plot is listed for these head calculations.
Mandatory Appendix 5, Fig 5 (material charts)
This pressure vessel calculator has been based upon versions of the ASME design code prior to ASME pulling Mandatory Appendix 5 for a rewrite. Therefore, the titles of each material chart associated with Fig 5 are provided below for your information (see Fig 7).
Fig. 5-UGO-28.0 Geometric chart for cylindrical vessels under external or compressive loadings (for all materials)
| Ductile Cast Iron: | |
|---|---|
| Fig. 5-UCD-28 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of cast ductile iron with a specified minimum yield strength of 40,000psi |
| Cast Iron: | |
|---|---|
| Fig. 5-UCI-28 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of cast iron |
| Carbon Steel | |
|---|---|
| Fig. 5-UCS-28.1 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of carbon or low alloy steels (specified minimum yield stress 24,000psi to but not including 30,000psi) |
| Fig. 5-UCS-28.2 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of carbon or low alloy steels (specified minimum yield stress 30,000psi and over except for materials within this range where other specified charts are referenced) and Type 405 and Type 410 stainless steels |
| Fig. 5-UCS-28.3 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of carbon steel, low alloy steels or steels with properties enhanced by heat treatment (specified minimum yield stress over 38,000psi for materials where other specific charts are not referenced) |
| Fig. 5-UCS-28.4 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of SA-537 |
| Fig. 5-UCS-28.5 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of SA-508 CL. 2 and 3, SA-533 CL. 1 Grades A, B, and C, SA-533 CL. 2 Grades A, B, C and D or SA-541 Grades 2 and 3 |
| Fig. 5-UCS-28.6 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of SA-562 or SA-620 carbon steel |
Asme Ug-80
Asme Ug 80
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | |
|---|---|
| Fig. 5-UHA-28.1 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of austenitic steel (18Cr-8Ni, Type 304) |
| Fig. 5-UHA-28.2 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of austenitic steel [18Cr-8Ni-Mo, Type 316; 18Cr-8Ni-Ti, Type 321; 18Cr-8Ni-Cb, Type 347; 25Cr-12Ni, Type 309 (through 1100°F only); 25Cr-20Ni, Type 310 and 17Cr, Type 430B stainless steel (through 700°F only)] |
| Fig. 5-UHA-28.3 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of austenitic steel (18Cr-8Ni-0.03 maximum carbon, Type 304L) |
| Fig. 5-UHA-28.4 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of austenitic steel (18Cr-8Ni-0.03 maximum carbon, Types 316L and 317L) |
| Fig. 5-UHA-28.5 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of Cr-Ni-Mo alloy (S31500) SA-669 |
| Quenched and Tempered Carbon and Low Alloy Steel | |
|---|---|
| Fig. 5-UHT-28.1 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of quenched and tempered low alloy steel, SA-517 all grades and SA-592 Grades A, E and F where t ≤ 2½ in |
| Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys | |
|---|---|
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.1 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of low carbon nickel |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.2 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 3003 in 0 and H112 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.3 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 3003 in 0 and H14 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.4 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 3004 in 0 and H112 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.5 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 3004 in 0 and H34 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.6 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.7 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of annealed nickel-copper alloy |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.8 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of annealed nickel-chromium-iron alloy |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.9 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of annealed copper Type DHP |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.10 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of annealed copper-silicon alloys A and C Type DHP |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.11 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of annealed 90-10 copper-nickel alloy |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.12 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of annealed 70-30 copper-nickel alloy |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.13 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 5154 in 0 and H112 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.14 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium bronze alloy 614 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.15 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-molybdenum alloy B |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.17 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 1060 in 0 temper |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.18 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 5052 in 0 and H112 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.19 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 5086 in 0 and H112 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.20 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 5456 in 0 temper |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.22 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of unalloyed titanium, Grade 3 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.23 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 5083 in 0 and H112 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.24 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-molybdenum-chromium-iron alloy |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.25 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-copper alloy |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.27 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-iron-chromium alloy 800 (annealed) |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.28 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of unalloyed titanium, Grade 2 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.29 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-iron-chromium alloy 800H (annealed) |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.30 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of welded aluminium alloy 6061-T6, T6510 and T6511 when welded with 5356 or 5556 filler metal all thicknesses; 4043 or 5554 filler metal, thickness ≤ ⅛ in |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.31 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of welded aluminium alloy 6061-T4, T451, T4510 and T4511 when welded with 4043, 5554, 5356 or 5556 filler metal all thicknesses; and of welded aluminium alloy 6061-T6, -T651, -T6510 and -T6511 when welded with 4043 or or 5554 filler metal, thickness > ⅜ in |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.32 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of aluminium alloy 5454 in 0 and H112 tempers |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.33 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-molybdenum-chromium alloy C-276 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.34 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of solution treated nickel-chromium-iron-molybdenum-copper (alloys G and G-2) |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.35 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of zirconium alloy 702 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.36 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of wrought chromium-nickel-iron-molybdenum-copper-columbium stabilized alloy SB-462, SB-463, SB-464, SB-468 and SB-473 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.37 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-iron-chromium-silicon alloy 330 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.38 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-chromium-molybdenum, alloy Grade C-4 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.39 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-molybdenum alloy X |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.40 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-molybdenum alloy B-2 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.41 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of zirconium alloy 705 (R60705) |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.42 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of titanium, Grade 1 |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.43 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed to welded copper-iron alloy tube C19400 (SB-543 welded) |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.44 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of annealed nickel-chromium-molybdenum-columbium alloy N06625 (SB-443, SB-444 and SB-446 in alloy 625) |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.45 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-molybdenum-chromium-iron-copper (Grade G-3) alloy G-3 whose thickness is ¾ in and under, having a minimum yield strength of 35ksi |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.46 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of nickel-molybdenum-chromium-iron-copper (Grade G-3) alloy G-3 whose thickness is greater than ¾ in and under, having a minimum yield strength of 30ksi |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.47 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of work-hardened nickel |
| Fig. 5-UNF-28.48 | Chart for determining shell thickness of cylindrical and spherical vessels under external pressure when constructed of SB-75 and SB-111light drawn seamless copper tubes, alloys C10200, C12000, C12200 and C14200 |
Applicability
This calculator applies to any internally or externally pressurised thin-wall cylindrical pressure vessel with formed head(s) according to the rules provided in ASME VIII, Division 1.
Accuracy
Accuracy is according to the rules provided in the ASME VIII, Division 1 design code
Notes
- Stored energy is a measure of the amount of energy that would be released in the event of a catastrophic failure
- ASME VIII recommends that all externally pressurised conical and toriconical heads with an included angle greater than 120° should be treated as flat heads, which are not included in Pressure Vessels
- Excluding nozzles and openings
- Elastic instability is amplified local deformation (strain) due to irregular shape
- The lower the stress at which failure will occur for a given external pressure
- ASME VIII, Division 1, Part UG
Factor 'A': Paragraph UG-23, (b) Step 1
Factor 'B': Paragraph UG-28, (c) Step 6; Pa = 4.B (where B is ASME yield stress) & Step 7; Pa = 2.A.E (where A is the strain factor and E is the Young's modulus {yield stress = A.E})
Asme Viii Ug-80
Further Reading
Asme Section Viii Ug 80
You will find further reading on this subject in reference publications(47)
